In vitro fertilization (IVF) is a complex yet effective assisted reproductive technology designed to help individuals and couples struggling with infertility achieve their dream of parenthood. The IVF process consists of several carefully coordinated steps, each playing a crucial role in ensuring the best possible outcome. This comprehensive guide will walk you through each step involved in the IVF process, providing insights into what to expect along the way.
1. Initial Consultation
The IVF journey begins with an initial consultation with a fertility specialist. During this appointment, the physician will review your medical history, conduct necessary tests, and discuss your fertility goals. This initial meeting is crucial for determining the underlying causes of infertility and whether IVF is the appropriate treatment option. Key components of the initial consultation include:
- Medical History Review: Discussing any previous fertility treatments, surgeries, and existing medical conditions.
- Physical Examination: Conducting a thorough physical examination, including a pelvic exam for women.
- Fertility Testing: Recommending various tests to assess ovarian reserve, hormone levels, sperm quality, and uterine health. Common tests may include blood tests, ultrasound evaluations, and semen analysis.
- Treatment Plan Discussion: Outlining the recommended IVF protocol based on the findings and addressing any questions or concerns you may have.
2. Ovarian Stimulation
Once you and your doctor decide to proceed with IVF, the next step is ovarian stimulation. This phase aims to stimulate the ovaries to produce multiple eggs, increasing the chances of successful fertilization. The key aspects of ovarian stimulation include:
2.1. Hormonal Medications
- Medications Prescribed: The physician will prescribe hormonal medications, typically gonadotropins, administered through daily injections. These hormones stimulate the ovaries to produce several mature eggs.
2.2. Monitoring
- Regular Monitoring: During this phase, you will undergo regular monitoring through blood tests and ultrasounds. Blood tests assess hormone levels, while ultrasounds monitor the growth and development of follicles (fluid-filled sacs containing eggs) in the ovaries.
2.3. Adjusting Medication
- Adjustments as Needed: Based on monitoring results, the doctor may adjust medication dosages to optimize follicle growth and ensure the best possible outcome.
3. Egg Retrieval
When the follicles have reached the appropriate size and the eggs are mature, the next step is egg retrieval. This minor surgical procedure typically takes place under sedation or anesthesia to ensure your comfort. The steps involved in egg retrieval include:
3.1. Preparing for Retrieval
- Pre-Procedure Instructions: You will receive instructions on how to prepare for the procedure, including dietary restrictions and medication guidelines.
3.2. Transvaginal Ultrasound Aspiration
- Procedure Description: During egg retrieval, a thin needle is guided through the vaginal wall into the ovaries using ultrasound imaging. The physician then aspirates (removes) the mature eggs from the follicles.
3.3. Recovery
- Post-Procedure Care: After the procedure, you will spend some time in recovery to ensure you are stable before being discharged. Some cramping and discomfort are normal, but most women feel well enough to resume normal activities within a day or two.
4. Sperm Collection
While the eggs are being retrieved, sperm is collected from the male partner or a sperm donor. The sperm collection process involves the following steps:
4.1. Sample Collection
- Obtaining the Sample: The sperm sample is typically collected through masturbation at the clinic. In some cases, sperm may be obtained through a surgical procedure if there are issues with sperm production.
4.2. Sperm Processing
- Laboratory Preparation: The collected sperm is processed in the laboratory to separate the most viable sperm from the sample. This preparation enhances the chances of successful fertilization.
5. Fertilization
Once the eggs and sperm are ready, the next step is fertilization. This critical phase involves the following procedures:
5.1. Traditional Insemination or ICSI
- Fertilization Methods: Fertilization can occur through traditional insemination, where the sperm is placed in a culture dish with the eggs and allowed to swim to the eggs, or through intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI). In ICSI, a single sperm is injected directly into an egg, which is often used in cases of male factor infertility.
5.2. Monitoring Embryo Development
- Embryo Culture: After fertilization, the resulting embryos are cultured in a controlled environment for several days, typically 3 to 5 days, to allow for optimal development.
6. Embryo Transfer
After monitoring embryo development, the next step is embryo transfer. This procedure involves placing one or more embryos into the uterus. The key components of the embryo transfer process include:
6.1. Preparing for Transfer
- Selection of Embryos: The physician will select the healthiest embryos for transfer based on quality and development stage. If there are surplus high-quality embryos, they may be frozen for future use.
6.2. Transfer Procedure
- Performing the Transfer: The embryo transfer procedure is a relatively simple and quick process. A thin catheter is used to place the selected embryo(s) into the uterus. This procedure is typically performed without anesthesia and can be done in the office setting.
6.3. Post-Transfer Care
- Aftercare Instructions: After the transfer, you may be advised to rest briefly before resuming normal activities. The doctor may provide specific post-transfer instructions to optimize your chances of implantation.
7. Pregnancy Testing
About 10 to 14 days after the embryo transfer, a pregnancy test is conducted to determine if implantation has occurred. The steps involved in this phase include:
7.1. Blood Test
- Beta-hCG Test: A blood test is performed to measure the level of human chorionic gonadotropin (beta-hCG), a hormone produced during pregnancy. A positive test indicates that implantation has occurred.
7.2. Follow-Up Care
- Next Steps: If the test is positive, you will be scheduled for follow-up appointments to monitor the early stages of pregnancy. If the test is negative, your doctor will discuss potential next steps and options for future cycles.
8. Potential Additional Steps
In some cases, additional steps may be involved based on individual circumstances:
8.1. Preimplantation Genetic Testing (PGT)
- Genetic Screening: If there are concerns about genetic disorders, preimplantation genetic testing (PGT) can be performed on embryos before transfer. This screening helps identify embryos with genetic abnormalities.
8.2. Cryopreservation
- Freezing Extra Embryos: Any surplus high-quality embryos that are not transferred can be cryopreserved (frozen) for future use, providing additional opportunities for pregnancy without the need for another full IVF cycle.
The IVF process is a multifaceted journey that requires careful planning and coordination among medical professionals, patients, and their families. Understanding the steps involved in IVF can help individuals and couples navigate this path more confidently. While the IVF journey can be challenging, many find that the potential for parenthood makes the effort worthwhile. As advancements in reproductive medicine continue to evolve, IVF remains a beacon of hope for those struggling with infertility. By being informed about the IVF process, prospective patients can better prepare themselves for the journey ahead and work closely with their healthcare team to achieve their dream of starting a family.
 Clinic Booking
Clinic Booking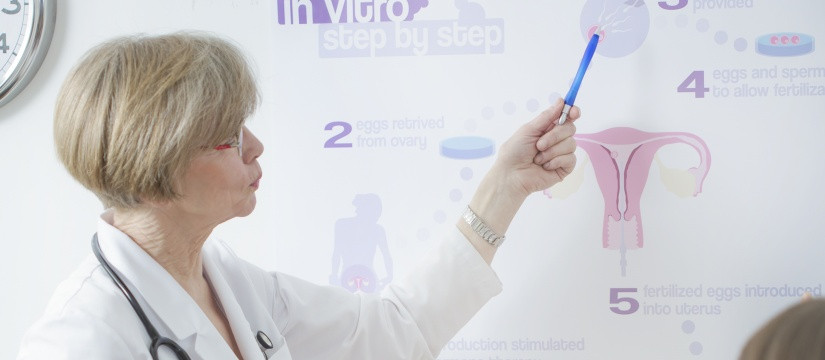


 No Record
No Record